
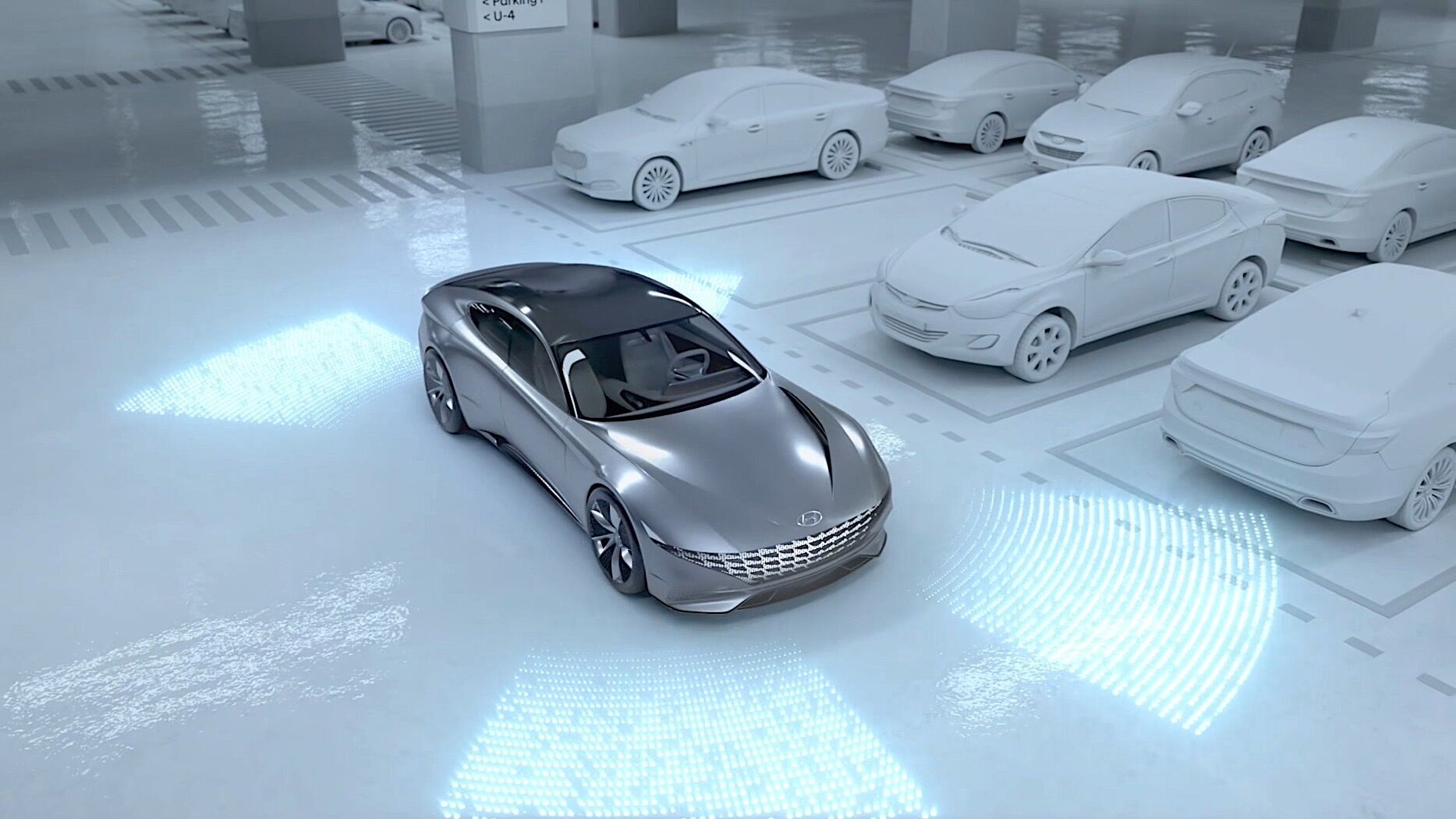
Many operations that seem to come easily in daily use are inseparable from the perception of sensors.
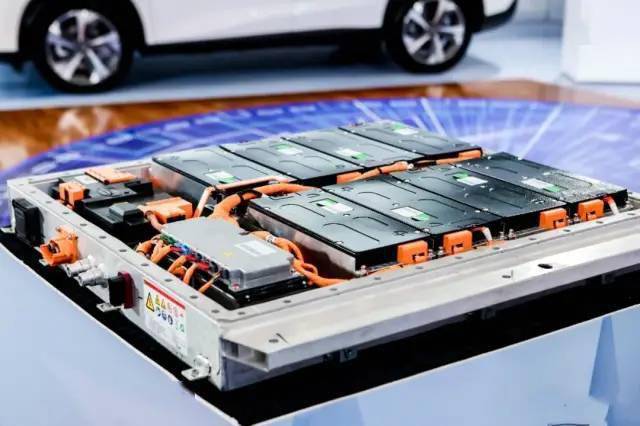

Double-side cooled (DSC) SiC modules show improvements in traction inverter performance compared to conventional single-side cooled (SSC) modules.

PassThru technology is an essential feature for wide input-powered devices. It allows for improved efficiency and extends the lifespan of energy storage systems vs. systems that utilize conventional control.

The growing use of electric vehicles has posed challenges for the electricity grid as it needs to meet the increased demand. This surge in electric vehicle adoption has brought about significant issues for power networks, such as higher power consumption, increased short-circuit currents, and the possibility of voltage fluctuations.

We see and hear about artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) everywhere these days. Some people claim that it will solve almost all our problems, just like the 5G hype a few years ago. Opinions range from the scariest invention in history to the most advanced technological advance imaginable, and many think it's a good thing, but there are plenty of concerns and caveats.

Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, often collectively referred to as AI technologies, are among the most heavily invested areas in modern times. It is predicted that in the next few years, AI technologies and capabilities will be integrated into a large number of edge devices and autonomous systems, and cloud-based and generative AI services will continue to increase.
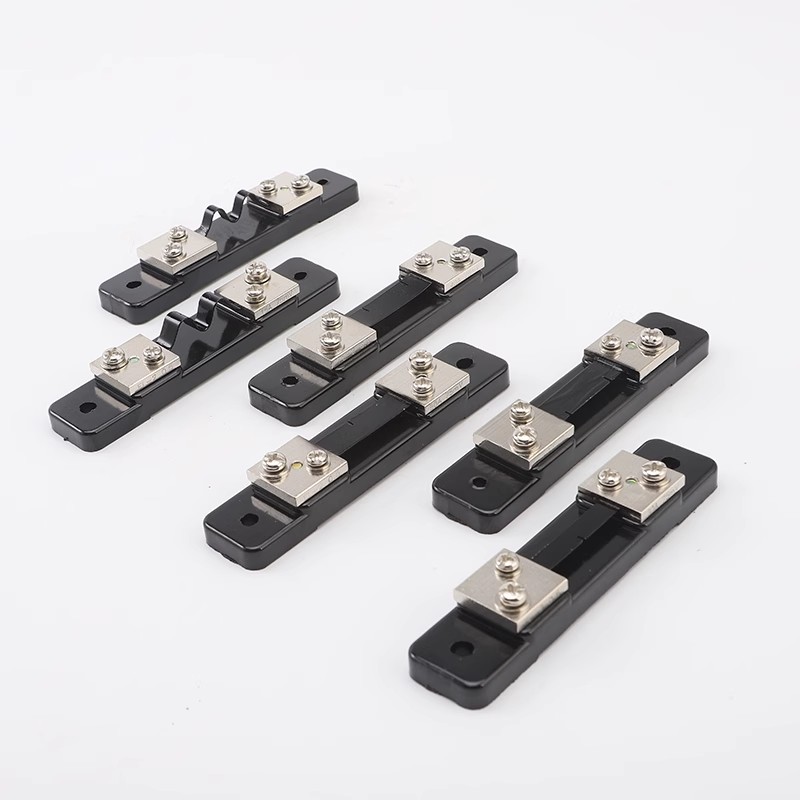

Current sensing technology plays a crucial role in various industries, where accurate and reliable measurements are essential for optimizing performance and ensuring system efficiency.

There are many different types of DC/DC converters, each with a unique mode of operation. The one proposed in this article involves the analysis of a DC/DC boost converter operating in Class E with dual-frequency signal drive. This solution allows the output power to be adjusted if the load should change.
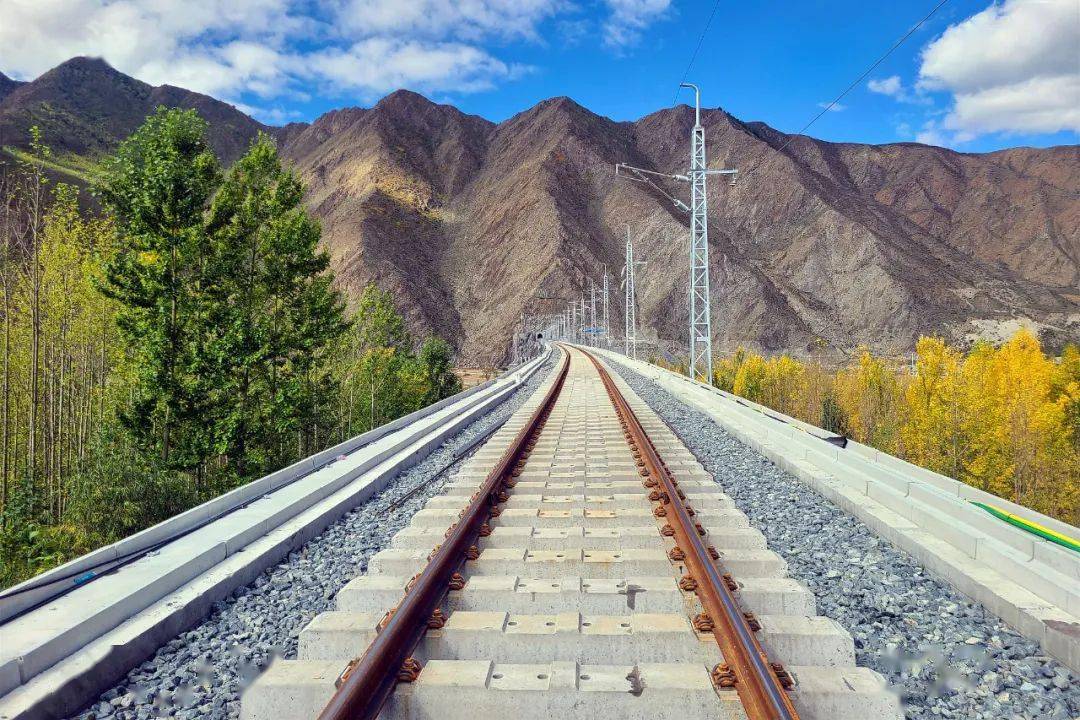

Railway electrification systems rely on a steady DC supply to both power their DC motors and the control/energy circuits. These DC-traction systems are more energy efficient than their coal, gas,or diesel-based counterparts while also reducing CO2 emissions.

When the post-COVID-19 era comes, the DC-DC converter applications will span a wide range of industries, including consumer electronics, medical, telecom/datacom, industrial, automotive, and railway rolling stock. The current growth at nearly 12% CAGR is accompanied by a strong push to save space, time, and cost toward application development.
The automotive industry’s evolution is leading to a growing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) that provide a more sustainable and environmentally friendly driving experience. However, to make EVs an affordable and accessible reality, the efficiency of the electronic components used for power conversion must be improved. In this context, 650V and 1200V high-power GaN devices are emerging as promising solutions.

Artificial intelligence (AI), a key driver for what is expected to be a trillion-dollar industry by 2030, is placing new focus on semiconductor performance. Some of the most complex problems in delivering next-generation AI capabilities come from device fabrication challenges that will need to be addressed by new etch technologies.

Power converter control plays a crucial role in optimizing the overall performance of power-conversion systems. With proper control, power converter efficiency can be maximized, energy losses reduced and component life improved. By designing sophisticated control algorithms, power transitions can be managed efficiently and optimally while keeping the power converter output voltage and current constant.
Robots have different applications in different markets and come in many forms, including service robots, collaborative robots (cobots), industrial robots, autonomous drones and autonomous guided vehicles. One of the key factors for the success of robotic applications is to ensure optimal motor driver design. Silicon-based motor drives require a compromise between efficiency and size.

The ease of use and convenience of electric vehicles is significantly affected by the way they are charged. Due to the limited number of high-power charging stations, a significant number of car owners still need to rely on on-board chargers (OBCs) to charge their electric vehicles. To improve the performance of on-board chargers, automakers are exploring new technologies such as carbonization (SiC). This technical article will explore the importance of in-car chargers and how advances in semiconductor switching technology are pushing the performance of in-car chargers to a whole new level.

With the advent of open floor plans for homes and offices and the growing shift to hybrid and electric vehicles, there is a growing need for quieter, more efficient motor control. Even very small acoustic differences can have a significant effect on audible noise.

The artificial intelligence (AI) revolution has arrived. With the public release of applications such as ChatGPT, people have been able to experience firsthand the power and potential of deep neural networks and machine learning (ML).

Traction inverters are the main component that consumes battery power in electric vehicles (EVs), with power levels up to 150kW or higher. The efficiency and performance of traction inverters directly affect the driving range of electric vehicles after a single charge. Therefore, in order to build the next generation of traction inverter systems, silicon carbide (SiC) field-effect transistors (FETs) are widely used in the industry to achieve higher reliability, efficiency and power density.